This guide explains how to find semantic keywords.
Below, you’ll find out how to identify semantic keywords and how to collect semantic keywords to improve the search engine optimization (SEO) for your website. You’ll learn how to use research tools like Google Trends and Semrush’s Keyword Planner to find good semantic keywords for your content.
By the end of the page, you should feel well-prepared to begin your semantic keyword research.

How to Find Semantic Keywords
1. Use Google Search
The first way for how to find semantic keywords is to start with Google itself. Semantic keywords are words or phrases related to an original search term and Google provides something similar to this directly in the search results.
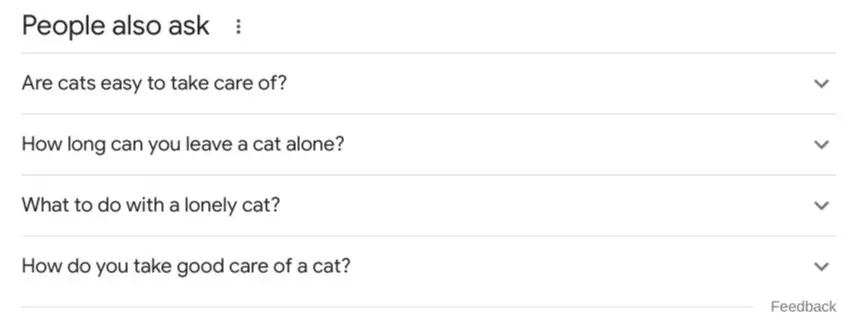
For example, typing in “how to look after a cat”” will bring up the usual search results, but it will also bring up the People Also Ask section as you can see in the example image below. These are semantically-related keyword phrases you can use as key sections in the content to enhance topical authority and expertise on the subject matter.
Scrolling down to the bottom of the Google search results brings up a set of alternative search terms called Related Searches like the following:
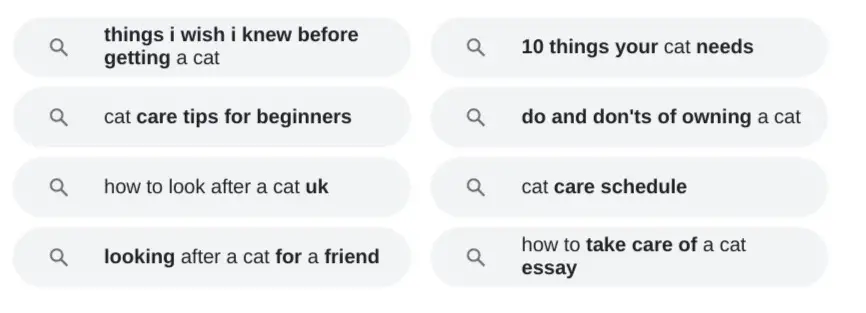
Those keyword suggestions are conceptually related to the main search term, and they can increase your understanding of what the user wants to find.
While not technically as accurate as specific semantic keyword research tools, looking at the Google Related Searches and People Also Ask tools can kickstart your research by giving you some ideas of related topics to include in the content or additional pages to create to boost topical authority.
By following this first step, you’ll gain a deeper insight into the motivation people have when searching for a certain topic. In the above example, people who look for cat care tips may also want to know if cats are easy to take care of, what are some good cat care tips for beginners, and which items a cat needs to be well cared for. And this information is a good start for planning high-quality and relevant content for your target audience.
2. Try Google Keyword Planner
The next for how to identify semantic keywords is to use Google Ads, which includes a useful tool called the Keyword Planner. Keyword Planner allows you to type in a term or phrase to bring up a list of similar words.
For example, typing in “cat care”‘ brings up keywords like “‘cat grooming”, “cat sitting”, and “newborn kittens” as you can see in the example image below.
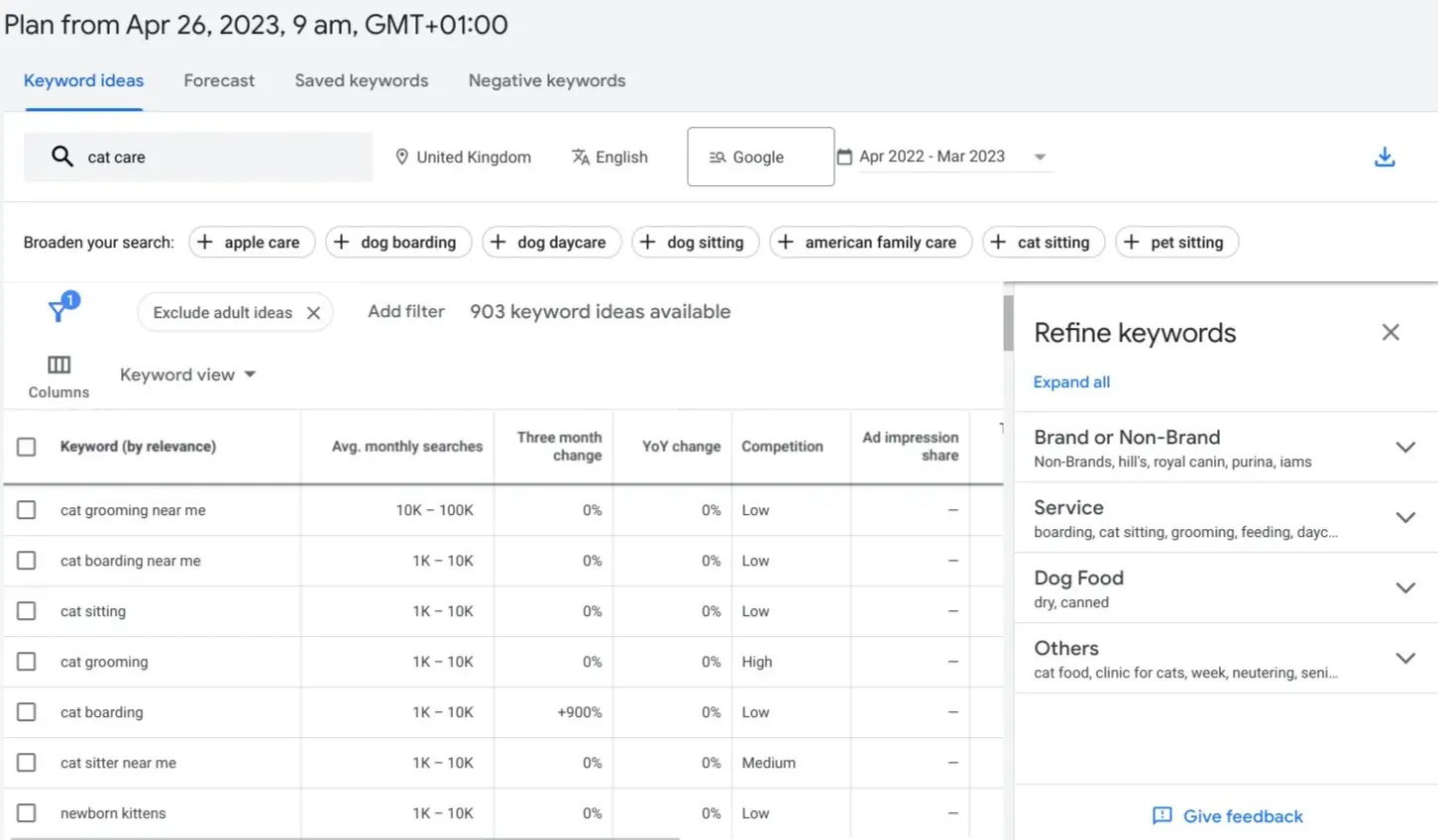
You can save these keywords and gain insight into the number of average monthly searches and the paid search competition for a particular semantically related keyword (ranked as low, medium, and high).
This is an easy way to collect semantic keywords for specific search terms and you to plan relevant and valuable content for your users. You can also avoid competitive search terms by focusing more on low or medium competition keywords.
3. Use an LSI Keyword Research Tool
LSI keyword research tools are software that is specifically designed to find the most relevant, semantically-related keywords to use in your content.
LSI is short for LSI Latent Semantic Indexing, and when you use a tool like this for keyword research, it takes your seed keyword and returns dozens of contextually related keywords to use for improved on-page SEO performance.
One of the most popular tools for this purpose is called LSIGraph, which works incredibly quickly at showing you the scores of semantically linked terms that are related to your primary keyword for SEO. SEO Powersuite and Twinword also have good software for semantic keyword research.
You can visit our related guide with a list of the best free LSI keyword generators & research tools to get started using this type of software for semantic SEO.
4. Open Google Trends
Google Trends is another good way to find semantic keywords. This tool helps identify patterns in how people search on Google. You can even narrow down to certain regions and periods of time to get even more specific, targeted data for SEO keyword research.
Google Trends also provides information about other key phrases people might be interested in. For example, searching for “‘cryptocurrency” in Google Trends brings up a selection of related topics as well as related queries as you can see in the example image below.
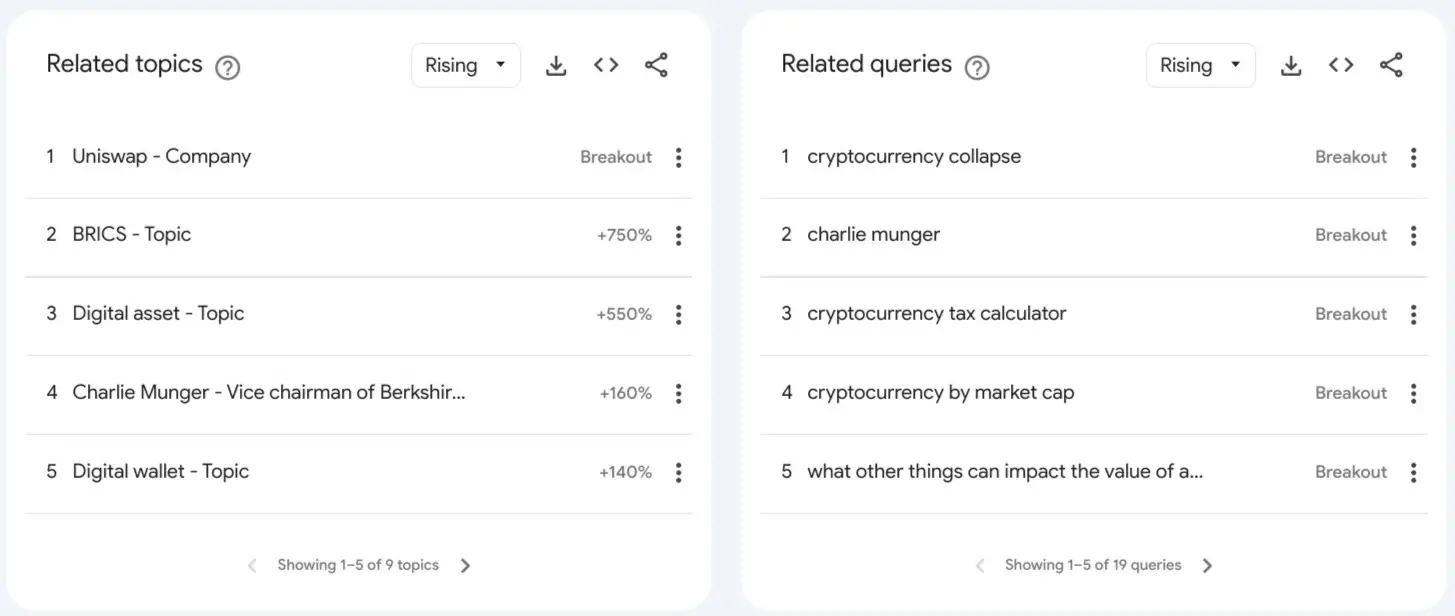
This data provides valuable information about what users are truly interested in, which is very helpful when planning content for your site. Plus, it’s free, straightforward, and gives in-depth data, regardless of your site’s niche.
Google Trends is also a handy tool if you want to think more locally. For example, if you run a local business, you can narrow down the searches to your specific region to get a clear idea of what your local customers are searching for online, allowing you to target your content specifically toward those individuals.
5. Use Semrush Keyword Magic Tool
Another tool you can consider for semantic keyword research is Semrush’s Keyword Magic tool. You can try it out for free using our affiliate link, plus get an extended free trial period.
This is a good solution for how to collect semantic keywords because Semrush has one of the largest, and most accurate, keyword databases in the world. After conducting a search, you can click on the “Related” tab to bring up a list of words that are closely related to your original search term.
The example image below shows this process in action when searching for the phrase, “yoga leggings”.
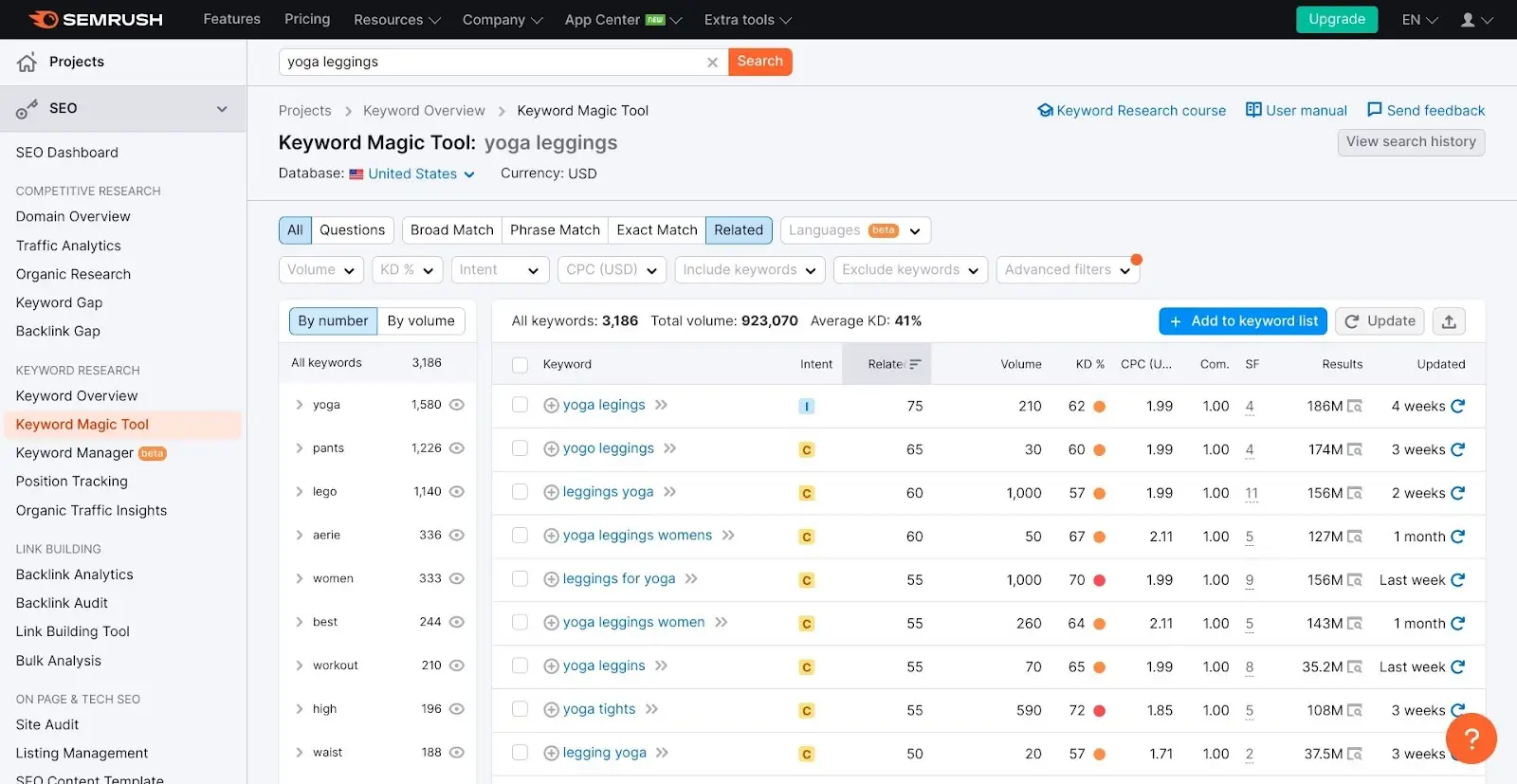
As you can see, this is a quick and easy way to collect semantic keywords and any one of these terms can be saved to a keyword list for future reference.
Additionally, keyword suggestions can be sorted by volume, difficulty, cost per click, and competitive density. This is very useful, as it allows you to focus on the keywords that are likely to perform well rather than focusing on very competitive or oversaturated keywords.
Semrush also has other powerful tools, including an on-page SEO checker, competitor analysis, and rank tracking, all of which are helpful if you’re trying to improve your site’s overall SEO strategy.
6. Find Keywords With Social Monitoring Tools
Social monitoring tools are another great way to collect semantic keywords. These tools will allow you to eavesdrop on social media networks, collecting real-life discussions about certain topics.
This is invaluable in terms of digging into the intent behind user searches and what they’re interested in online. Social media monitoring tools allow you to understand public opinion on certain topics and discover the needs of your target audience.
A few social monitoring tools that can help you with this process include:
Some of these tools offer free trials, so you can give them a try to see if they work for you and the goals of your site before making a financial commitment.
Learn More About Semantic Keywords
The links below explain more about semantic keywords and how to use them effectively for search engine optimization. Use these resources to expand your knowledge on the subject.
- Semantic Keyword Research Explained
- Best Semantic SEO Tools
- Best Free LSI Keyword Generators & Research Tools
- Semantic Search vs Keyword Search
Find Semantic Keywords Summary
We hope you enjoyed this guide on how to find semantic keywords.
As you discovered, there are several good solutions to identify semantic keywords, such as Google Search, Google Trends, Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, and social media monitoring tools. And each option offers a unique way for how to collect semantic keywords to improve your website’s SEO strategy.

The Editorial Staff at SEO Chatter is a team of search engine optimization and digital marketing experts led by Stephen Hockman with more than 15 years of experience in search engine marketing. We publish guides on the fundamentals of SEO for beginner marketers.
